Login
Subscribecell & molecular biology, disease & medicine, genetics & genomics

Early-Life Stress Exerts Long-Lasting Effects Via Epigenome
Asher Jones | Mar 18, 2021 | 5 min read
In mice, epigenetic marks made on histones during infancy influence depression-like behavior during adulthood. A drug that reverses the genomic tags appears to undo the damage.

Genetic Reprogramming Restores Vision in Mice: Study
Max Kozlov | Dec 6, 2020 | 5 min read
Researchers repaired what is otherwise irreversible damage in the animals’ ocular neurons, by activating transcription factors ordinarily used to generate induced pluripotent stem cells.

Molecular Biologist Jeff McKnight Dies at 36
Amanda Heidt | Oct 8, 2020 | 3 min read
The University of Oregon scientist studied the structure and function of chromatin, with the intent of designing new therapeutic tools.

Stomach Acid & Heartburn Drugs Linked with COVID-19 Outcomes
Ashley Yeager | Oct 7, 2020 | 6 min read
While sick with COVID-19, President Trump is taking an antacid. Doctors have been exploring whether these medicines can treat SARS-CoV-2 infections, and the results are mixed.

SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Shares Sequence with a Human Protein
Abby Olena, PhD | Jun 1, 2020 | 3 min read
Eight amino acids are identical to part of the human epithelial sodium channel, leading researchers to suspect the virus might interfere with the channel’s function.

Infographic: How Some X-Chromosome Genes Escape Inactivation
Amber Dance | Mar 1, 2020 | 2 min read
About one-quarter of the hundreds of genes on the inactivated X chromosome in XX cells manage to escape that silencing, at least some of the time.

Genes that Escape Silencing on the Second X Chromosome May Drive Disease
Amber Dance | Mar 1, 2020 | 10+ min read
When X-linked genes evade silencing on the “inactive” chromosome in XX cells, some protect women from diseases such as cancer, but others seem to promote conditions such as autoimmunity.

Infographic: How Does Cell Senescence Drive Aging and Disease?
Katarina Zimmer | Mar 1, 2020 | 4 min read
The accumulation of zombie-like cells seems to accelerate aging and promote aging-related disease. Researchers are trying to figure out how.

Inadequate Myelination of Neurons Tied to Autism: Study
Lisa Winter | Feb 4, 2020 | 2 min read
A mouse model of autism and postmortem brains of autistic individuals showed a lack of mature oligodendrocytes and less myelination than controls.
Circulating Fetal Cells Sequenced for Prenatal Testing Study
Emily Makowski | Dec 10, 2019 | 3 min read
Trophoblasts, collected from the mother during a blood draw, can determine fetal genetic abnormalities currently diagnosed through amniocentesis or chorionic villi sampling.

Cigall Kadoch Unravels Chromatin’s Role in Cancer
Chia-Yi Hou | Sep 1, 2019 | 3 min read
The Dana-Farber Cancer Institute researcher is developing cancer therapeutics based on how the physical structure of DNA contributes to the disease.
Exercise Changes Our Gut Microbes, But How Isn’t Yet Clear
Ashley Yeager | Aug 15, 2019 | 5 min read
Physical activity, independent of diet, shifts the composition of bacteria in the intestines, spurring researchers to search for species that might provide benefits akin to working out.

Astronaut Study Shows Some Lasting Changes from Time in Space
Kerry Grens | Apr 11, 2019 | 2 min read
Scott Kelly’s physiology, gene activity, and mental performance changed after time aboard the International Space Station, but mostly returned to normal once back on Earth.

Reprogrammed Müller Glia Restore Vision in Mice
Ashley Yeager | Aug 15, 2018 | 4 min read
A double gene-transfer therapy transformed the non-neuronal cells into rod photoreceptors in the retinas of animal models of congenital blindness.
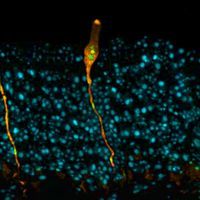
New Lung Cell Identified
Abby Olena, PhD | Aug 1, 2018 | 4 min read
The cell type was discovered via single-cell RNA sequencing of thousands of cells in mouse and human airways and may play a role in cystic fibrosis.

Image of the Day: New Kids on the Block
Sukanya Charuchandra | Jun 7, 2018 | 1 min read
Researchers discover that a layer of human breast tissue is not one but two distinct cell types.
