The immune system is a complex network that recognizes internal and external threats and activates specific responses to protect the body.1 Immune tolerance is a hallmark of proper immune function, as it underpins the immune system’s ability to tell friend from foe. This tolerance relies on several checkpoints that downregulate or remove potentially self-harmful elements. For example, the thymus removes lymphocytes that attack self molecules prior to maturation, while regulatory T cells suppress self-reacting mature T cells in the periphery.2
These systems, while comprehensive, are not failproof. Immune system malfunctions can result in autoimmunity, where the immune system attacks self-cells or tissues. To date, scientists have identified over 100 distinct autoimmune disorders. These diseases can be systemic in nature or limited to specific organs, but they comprise some of the most common conditions afflicting humans, including type 1 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease.1
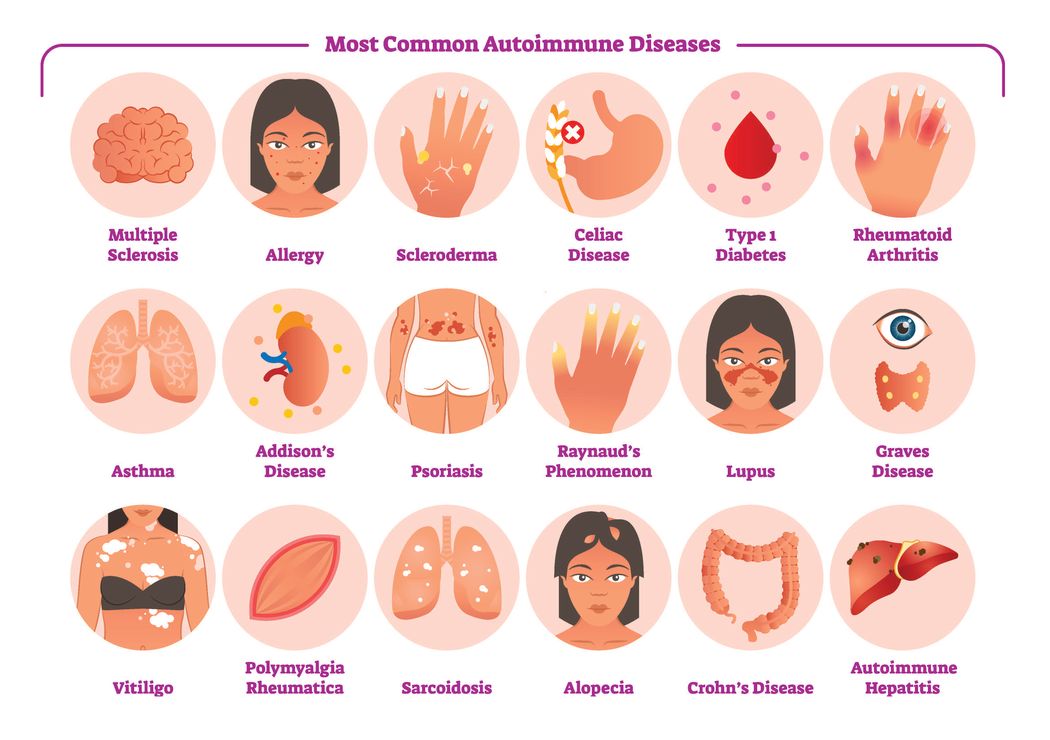
Autoimmune diseases represent a significant health burden.
Sino Biological
The immune system possesses a great deal of diversity and variation, which gives it the flexibility to identify and combat a wide range of pathogens. However, this also creates more opportunities for self-targeting cells to slip through the cracks, and it makes it more difficult for researchers to pinpoint the underlying causes of autoimmune disorders.3 Given this, autoimmune disease research currently centers on characterizing and delineating the molecular basis behind immune system dysfunction. Researchers rely on reagent suppliers such as Sino Biological to provide a comprehensive suite of tools, including recombinant target proteins, cytokines, and kinases, as well as antibodies and ELISA kits, to identify biomarkers for disease diagnosis and therapeutic targets for improving treatment precision and effectiveness.
Read more about why having a diverse range of reagents is important for autoimmune disease research.
References:
- Wang L, et al. J Intern Med. 2015;278(4):369-95.
- Shirafkan F, et al. Front Immunol. 2024;15:1339714.
- Liston A, et al. Nat Immunol. 2021; 22:1479-89.

