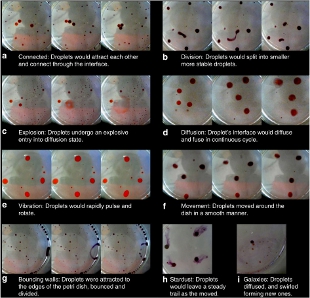
 Examples of different oil droplet behavior observed in the experimentImage from Nature CommunicationsIt’s not exactly survival of the fittest, but researchers in Scotland have shown that oil droplets can exhibit a rudimentary form of evolution. The nonbiological system comprised more than 200 different droplet types composed of four chemicals that exhibited predictable behaviors when dropped into petri dishes full of water. The scientists analyzed the droplets’ fitness based on those behaviors, and found that they could direct the evolution of more stable droplets.
Examples of different oil droplet behavior observed in the experimentImage from Nature CommunicationsIt’s not exactly survival of the fittest, but researchers in Scotland have shown that oil droplets can exhibit a rudimentary form of evolution. The nonbiological system comprised more than 200 different droplet types composed of four chemicals that exhibited predictable behaviors when dropped into petri dishes full of water. The scientists analyzed the droplets’ fitness based on those behaviors, and found that they could direct the evolution of more stable droplets.
Glasgow University chemist Lee Cronin, who led the work, told WIRED.co.uk that the experiment is an important demonstration of the principles that may have spurred nonliving components to give rise to living things. “Right now, evolution only applies to complex cells with many terabytes of information but the open question is where did the information come from?” he said. “We have shown that it is possible to evolve very simple chemistries with little information.” (See “RNA World 2.0,” The Scientist, March 2014.) Cronin and his colleagues published the work yesterday (December 8) in Nature Communications.
The researchers used a robot based on a simple 3-D printing platform that created oil droplets at random from combinations of four different chemicals—1-octanol, diethyl phthalate, 1-pentanol, and either octanoic ...













