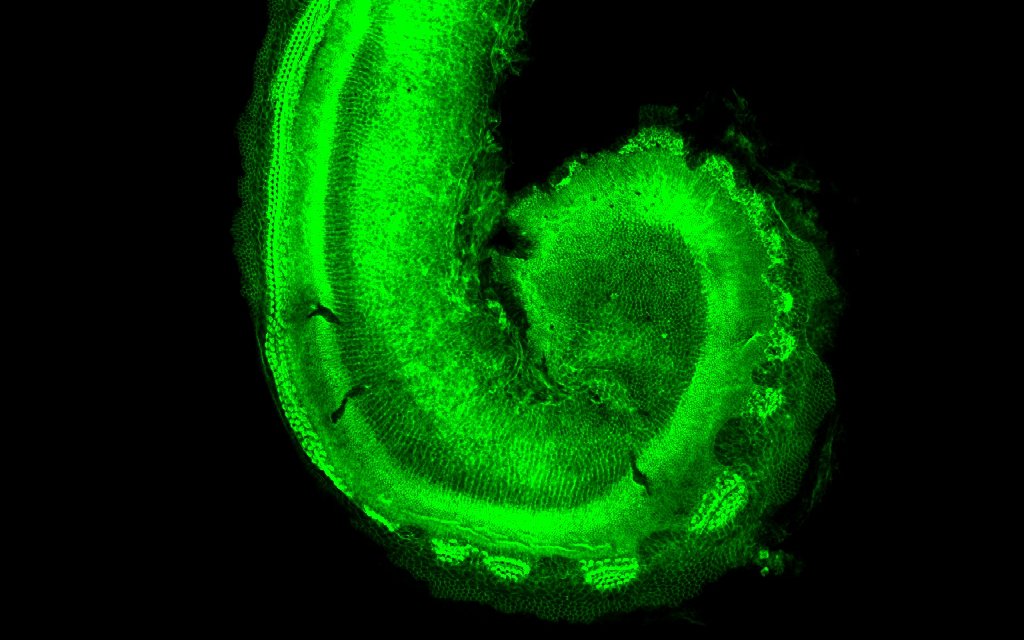
 Cochlea showing hair cellsFLICKR, ELIFEWe’re born with about 15,000 hair cells within each of our inner ears. These specialized cells that detect sound waves and help us maintain balance. Throughout our lives, these cells become damaged, contributing to hearing loss. Unlike fish, birds, and reptiles, humans are incapable of regenerating these important cells.
Cochlea showing hair cellsFLICKR, ELIFEWe’re born with about 15,000 hair cells within each of our inner ears. These specialized cells that detect sound waves and help us maintain balance. Throughout our lives, these cells become damaged, contributing to hearing loss. Unlike fish, birds, and reptiles, humans are incapable of regenerating these important cells.
But now, a February 21 study in Cell Reports describes an innovative method for regenerating large numbers of hair cells from mouse stem cells in vitro. “Hearing loss is a real problem as people get older,” said coauthor Robert Langer of MIT in a press release. “It’s very much of an unmet need, and this is an entirely new approach.”
Langer and colleagues built upon the results of a 2013 Neuron paper, in which a separate team described producing hair cells from mouse stem cells, but only in small quantities (to the tune of 200 cells). With their revised technique, which involves additional molecules that stimulate the Wnt pathway to coax stem cells, Langer and colleagues reported producing more than 11,000 hair cells.
“We only ...




















