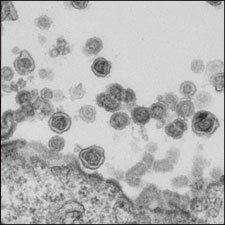
 |
Image: Whittmore Peterson Institute |
**__Related stories:__***linkurl:Viral cause for prostate cancer?;http://www.the-scientist.com/news/display/55966/
[7th September 2009]*linkurl:The virus hunter;http://www.the-scientist.com/article/display/54041/
[January 2008]*linkurl:The infection-chronic disease link strengthens;http://www.the-scientist.com/article/display/12009/
[4th September 2000]

















