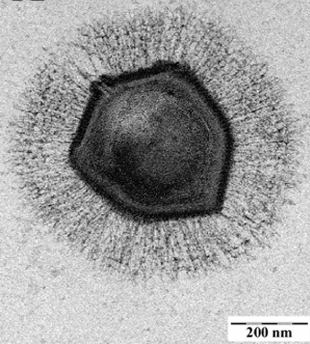
 Electron microscopic image of a mimivirus, the first type of giant virus discoveredWIKIMEDIA, E. GHIGO ET AL.Discoveries of viruses with physical and genomic dimensions that challenge the very definition of these infectious agents—the so-called giant viruses—have made headlines for more than a decade now. And they’ve made the news once again this week (March 3), with the publication in PNAS of a new species that a team led by researchers at Aix-Marseille University in France discovered buried in the permafrost of Siberia.
Electron microscopic image of a mimivirus, the first type of giant virus discoveredWIKIMEDIA, E. GHIGO ET AL.Discoveries of viruses with physical and genomic dimensions that challenge the very definition of these infectious agents—the so-called giant viruses—have made headlines for more than a decade now. And they’ve made the news once again this week (March 3), with the publication in PNAS of a new species that a team led by researchers at Aix-Marseille University in France discovered buried in the permafrost of Siberia.
The new virus, dubbed Pithovirus sibericum, measures 1.5 μm in length and 0.5 μm in diameter—even bigger than former record holders, the pandoraviruses, which are only 1 μm long and 0.5 μm in diameter. P. sibericum was identified as part of a survey of the virome of Siberian permafrost, isolated from a sample that’s more than 30,000 years old, according to the researchers. Nevertheless, when given access to an amoeba host in the lab, P. sibericum infected the cell, raising concerns about the possible risk such giant viruses might pose if they are released from the thawing Arctic ground.
“The revival of such an ancestral amoeba-infecting virus . . . suggests that the thawing of permafrost either from global warming or industrial exploitation of circumpolar ...
















