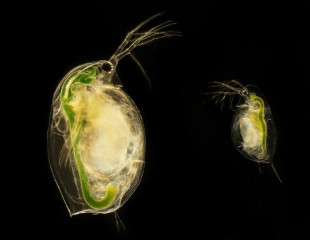
 Adult female Daphnia magna (left) and D. dentifera (right)ISABELLA OLESKY (COURTESY OF CATHERINE SEARLE)Chytridiomycosis, the deadly disease caused by the fungal pathogen Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis (Bd), has been decimating amphibian populations worldwide since the 1980s. “We have no means to stop its advance,” said Antje Lauer, a microbial ecologist at California State University in Bakersfield, “and no cure that can be used in the wild to protect amphibians from it.”
Adult female Daphnia magna (left) and D. dentifera (right)ISABELLA OLESKY (COURTESY OF CATHERINE SEARLE)Chytridiomycosis, the deadly disease caused by the fungal pathogen Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis (Bd), has been decimating amphibian populations worldwide since the 1980s. “We have no means to stop its advance,” said Antje Lauer, a microbial ecologist at California State University in Bakersfield, “and no cure that can be used in the wild to protect amphibians from it.”
Bd affects amphibian skin, disrupting its ability to regulate electrolytes in the body, explained Jamie Voyles, an infectious disease ecologist at New Mexico Tech. Infected frogs lose excessive amounts of sodium and potassium, which are critical to keep their hearts pumping. Eventually, their hearts stop.
But new research suggests a potential preventive agent against Bd infection—one that may already be swimming all around the affected amphibians. Two recent studies demonstrated that aquatic microscopic fauna—such as Daphnia, Paramecium, and rotifers—can consume free-floating Bd zoospores, keeping Bd from infecting as many frogs.
Dirk Schmeller, a conservation biologist at the Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research in Germany, knew that Bd infection rates varied greatly across frog populations in lakes within the Pyrenees mountains, between France and Spain. Curious ...













