Neurotransmitters are the words our brain cells use to communicate with one another. For years, researchers relied on tools that provided limited temporal and spatial resolution to track changes in the fast chemical chat between neurons. But that started to change about ten years ago for glutamate—the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in vertebrates that plays an essential role in learning, memory, and information processing—when scientists engineered the first glutamate fluorescent reporter, iGluSnFR, which provided a readout of neurons’ fast glutamate release.
The Birth of Glutamate Biosensors
In 2013, researchers at the Howard Hughes Medical Institute collaborated with scientists from other institutions to develop the first generation of the glutamate biosensor iGluSnFR.1 To create the biosensor, the team combined a bacteria-derived glutamate binding protein, Gltl, a wedged fluorescent GFP protein, and a membrane-targeting protein that anchors the reporter to the surface of the cell. Upon glutamate binding, the Gltl protein changes its conformation, increasing the fluorescence intensity of GFP.
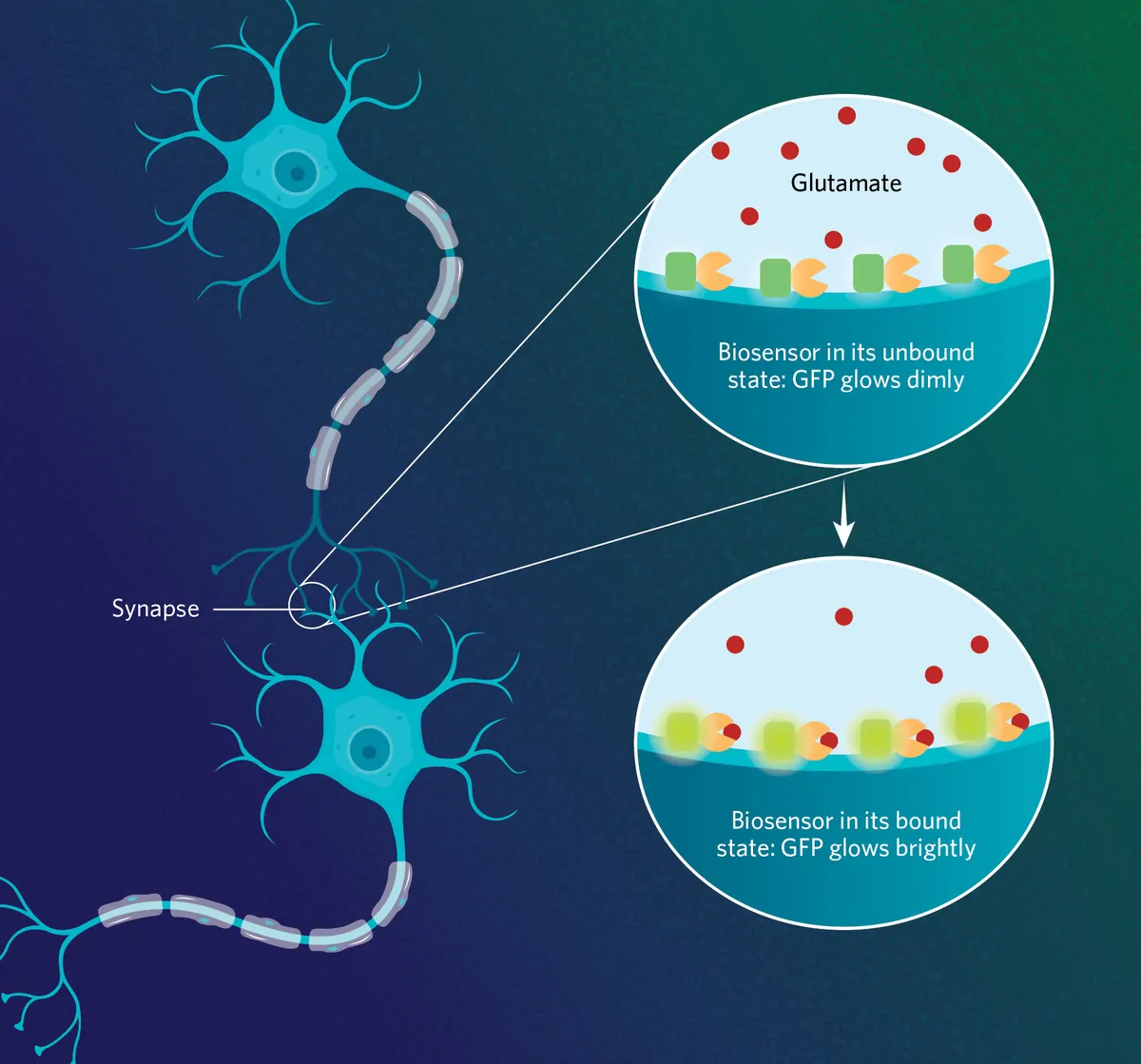
The third generation of glutamate sensors, iGluSnFR3, tracks glutamate release at the synapse level. Upon binding to glutamate, the reporter changes its conformation, intensifying the signal of its fluorescent protein. WEB | PDF
© ISTOCK.COM, wetcake, Designed by Ashleigh Campsall
In their first study, the team showcased the utility of the biosensor for monitoring glutamate levels by demonstrating selective activation by glutamate in cell cultures. By conducting experiments with brain cells from the C. elegans worm, zebrafish, and mice, they confirmed that the reporter also tracked glutamate in vivo, a finding that set iGluSnFR apart from existing glutamate sensors.
The first generation glutamate sensor allowed researchers to study glutamate dynamics in different biological systems, but the indicator could not detect small amounts of the neurotransmitter or keep up with brain cells’ fast glutamate release bouts.
Making Improvements
To overcome those limitations, the researchers came up with the second generation of reporters, dubbed SF-iGluSnFR. For these new indicators, they swapped the type of GFP protein, producing a more photostable reporter with a brighter fluorescent signal. They also altered one amino acid in the glutamate binding protein, improving the indicator’s sensitivity to tiny amounts of glutamate, and developed variants with different glutamate affinities, expanding the applications of the biosensors.2
Scientists have waited for fluorescent reporters for the major neurotransmitters in the brain, and the greatest progress has been made with these iGluSnFR sensors, said Edwin Chapman, a biochemist at the University of Wisconsin-Madison who helped characterize the second-generation glutamate biosensors. “Most generations have multiple versions, and different versions are useful for different purposes,” he added.
Despite the improvements, the second-generation SF-iGluSnFR biosensor still lacked resolution for monitoring glutamate release at the synapses. “Although these indicators were sort of revolutionary, the first readout you got from using them was not specific to synaptic response only,” said Abhi Aggarwal, a molecular biologist and protein engineer at the Allen Institute for Neural Dynamics. To bring the reporter a step closer to tracking the fast glutamate release where it happens, Aggarwal, in collaboration with some of the former glutamate sensor creators, developed the third generation of these indicators (iGluSnFR3).3
“We wanted to develop an indicator that only lights up when synaptic transmission is happening and not detect glutamate that has diffused away from nearby processes,” Aggarwal said.
To understand the complexity of synaptic inputs is totally impossible with other methods. The idea, in principle, with a glutamate sensor is that you really see the special glutamate signal.
—Andrew Plested, Humboldt University of Berlin
Using one of the second-generation biosensors as a template, the researchers performed an extensive screening of iGluSnFR variants in bacteria and found one with kinetic and photophysical features that hinted at improved synaptic-specific signals. The team next investigated how the iGluSnFR3 signal relates to the electrical activity of neurons, which associates with neurotransmitter release, in intact brains. For this purpose, the researchers imaged individual synapses of neurons in the mouse visual cortex while simultaneously recording their spontaneous electrical activity. The glutamate indicator signal linked to transient single action potentials with high specificity, suggesting that the biosensor detects electrical changes associated with glutamate release.
Studying neurons with thousands of synapses is not an easy feat, yet the latest version of iGluSnFR will likely help scientists to gain further insight into these complex systems, said Andrew Plested, a neuroscientist at Humboldt University of Berlin whose research focuses on glutamate receptors. “To understand the complexity of synaptic inputs is totally impossible with other methods. The idea, in principle, with a glutamate sensor is that you really see the special glutamate signal,” he added.
Looking Forward
As a presynaptic biologist, Chapman is excited about how these biosensors can accelerate the rate of progress in his field of study. For instance, iGluSnFR reporters can help neuroscientists understand better how glutamate is released by the neurons since there are different forms of release, he explained. “They have incredible sensitivity and temporal resolution to discriminate between different temporal components of release such as fast versus slow,” he said.
For Aggarwal, whose work focuses on developing neural imaging tools, the development of neurotransmitter-based indicators like iGluSnFR is key to advance the understanding of how neurons work. “We need to be able to detect when that communication is happening so that we can better understand how neurons are communicating.”
FAQ
What are neurotransmitters?
- As critical chemical messengers involved in sensation, memory, and movement, neurotransmitters are the words that our brain cells use to communicate with one another and the rest of the body.
What does glutamate do to the body?
- The amino acid glutamate is the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in vertebrates. It is synthesized in the central nervous system and plays an essential role in learning, memory, and information processing.
How do glutamate biosensors work?
- Researchers developed the first glutamate fluorescent reporter, iGluSnFR using a bacteria-derived glutamate binding protein, a wedged fluorescent GFP protein, and a membrane-targeting protein that anchors the biosensor to the surface of the cell. Upon binding to glutamate, the reporter changes its conformation, intensifying the signal of its fluorescent protein. Subsequent generations of glutamate sensors use similar but improved mechanisms to track glutamate release at the synapse level.
This article was originally published on September 8, 2023. It was updated on February 20th, by Deanna MacNeil, PhD.
- Marvin JS, et al. An optimized fluorescent probe for visualizing glutamate neurotransmission. Nat Methods. 2013;10(2):162-170.
- Marvin JS, et al. Stability, affinity, and chromatic variants of the glutamate sensor iGluSnFR. Nat Methods. 2019;16(2):206.
- Aggarwal A, et al. Glutamate indicators with improved activation kinetics and localization for imaging synaptic transmission. Nat Methods. 2023;20(6):925-934.















