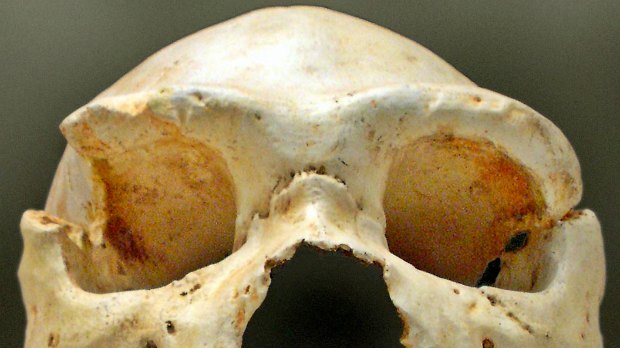
 WIKIPEDIA, JOSE-MANUEL BENITO ALVAREZThe collection of ancient-human remains at the Sima de los Huesos cave in Spain has led scientists to rewrite the timeline for human history—again. Using nuclear DNA extracted from the 430,000-year-old bones of two individuals, researchers determined that the bones belonged to Neanderthals, who must have split previously from the predecessor they share with Denisovans, another ancient-human group.
WIKIPEDIA, JOSE-MANUEL BENITO ALVAREZThe collection of ancient-human remains at the Sima de los Huesos cave in Spain has led scientists to rewrite the timeline for human history—again. Using nuclear DNA extracted from the 430,000-year-old bones of two individuals, researchers determined that the bones belonged to Neanderthals, who must have split previously from the predecessor they share with Denisovans, another ancient-human group.
Earlier mitochondrial analyses of ancient DNA sourced from the site suggested the inhabitants were related to Denisovans, perhaps representing a common predecessor of Neanderthals and Denisovans.
In this latest study, published today (March 14) in Nature, Matthias Meyer of the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig, Germany, and colleagues examined nuclear DNA. The genetic material revealed that the bones were related to Neanderthals, and not Denisovans. However, Meyer and his colleagues wrote in their report, “mitochondrial DNA recovered from one of the specimens shares the previously described relationship to Denisovan mitochondrial DNAs, suggesting, among other possibilities, that the mitochondrial DNA gene pool of Neanderthals turned over later in their history.”
Chris Stringer, a palaeoanthropologist at the Natural History Museum in London, told Science ...














