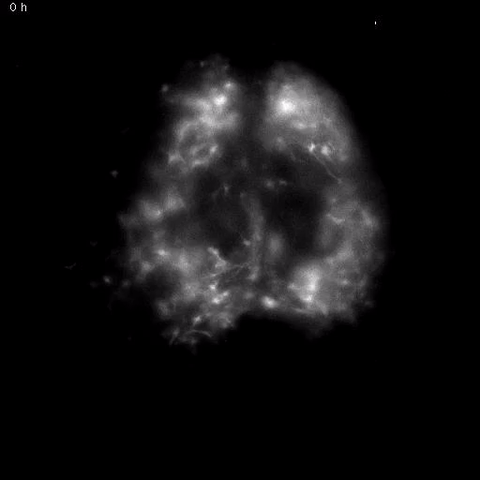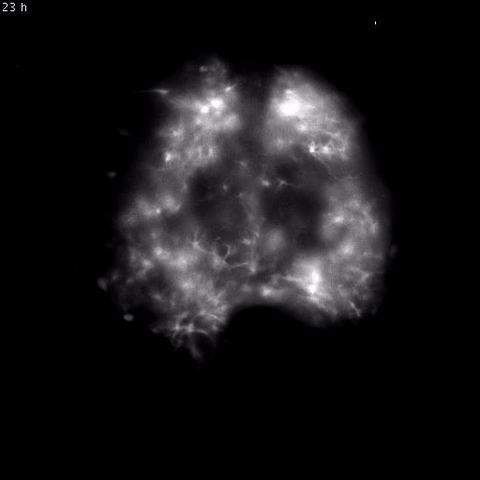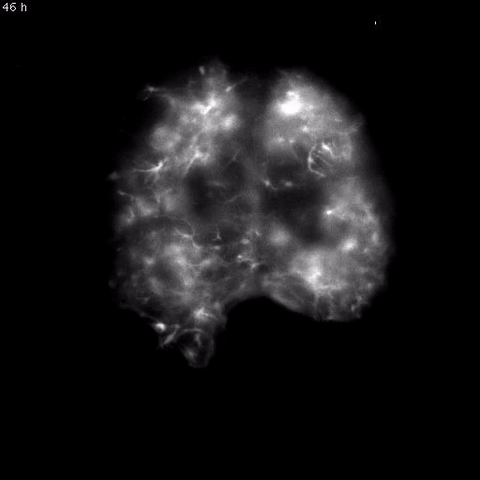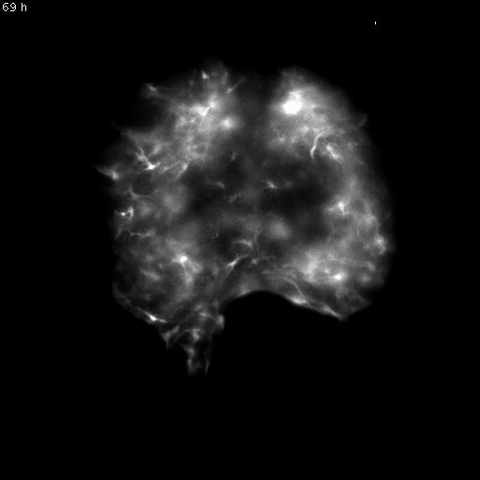
 Time-lapse video of daily rhythms in Bmal1 expression in murine SCN astrocytesHERZOG LAB, WASHINGTON UNIERSITY IN ST. LOUIS
Time-lapse video of daily rhythms in Bmal1 expression in murine SCN astrocytesHERZOG LAB, WASHINGTON UNIERSITY IN ST. LOUIS
Astrocytes, star-shape glial cells in the brain, were once simply considered support cells for neurons. However, neuroscientists have recently realized they have many other functions: studies have shown that astrocytes are involved in metabolism, learning, and more. In the latest study to investigate astrocytes’ roles in the brain, researchers confirmed these cells played a key role in regulating mouse circadian rhythms. The team’s results were published today (March 23) in Current Biology.
“Recent results have indicated that [glia] are actively modulating synaptic transmission, the development of the nervous system, and changes in the nervous system in response to changes in the environment,” said coauthor Erik Herzog, a neuroscientist at Washington University in St. Louis. “So circadian biologists recognized that the system that we study in ...














