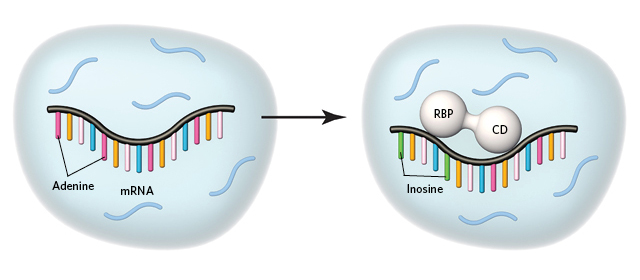
TRIBE method for identifying RNAs that interact with ribosome-binding proteins (RBPs) fuses an RBP of interest to the catalytic domain (CD) of an RNA-editing enzyme. When the RBP-CD fusion protein binds to the RBP’s specific RNA targets, the CD converts adenine nucleotides to inosine nucleotides. Extraction and RNA sequencing thus reveals those RNAs with altered sequences.
 © GEORGE RETSECKRNA Tagging fuses an RBP of interest to an enzyme that attaches chains of uridines (U) to the ends of the RBP’s target RNAs. The poly-U tails are then used to identify targets during RNA sequencing.
© GEORGE RETSECKRNA Tagging fuses an RBP of interest to an enzyme that attaches chains of uridines (U) to the ends of the RBP’s target RNAs. The poly-U tails are then used to identify targets during RNA sequencing.  © GEORGE RETSECK
© GEORGE RETSECK
Read the full story.


















