 B. salamandrivoransPNAS, MARTEL ET AL.
B. salamandrivoransPNAS, MARTEL ET AL.
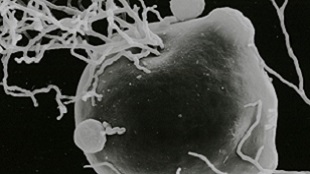
More than 200 frogs, toads, and other amphibian species around the world are threatened by a lethal skin disease caused by the chytrid fungus Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis (Bd). Last year, a related pathogen was discovered decimating populations of fire salamanders in the Netherlands and Belgium. The new microscopic killer, known as B. salamandrivorans (Bs), is only the second known species of its kind found to infect vertebrate hosts.
Now, an analysis of more than 5,000 amphibians from four continents suggests that Bs may have spread from Asia to Europe through pet trade. The results, published today (October 30) in Science, also reveal the extent to which other amphibian species are vulnerable to the fungus. So far, European newts and salamanders appear to be the most severely ...




















