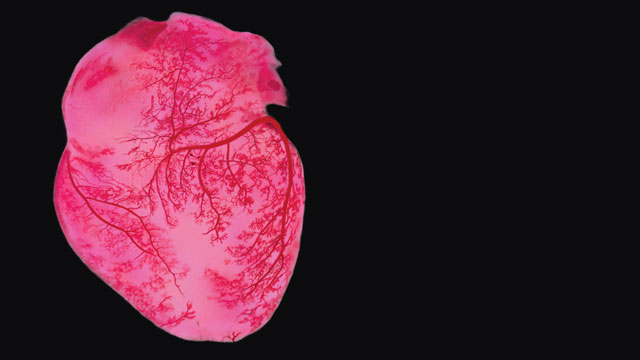
 LIFELINES: The arteries and veins of the human heart (shown here injected with dyed gelatin) are critical to the organ’s function, with blood flow delivering life-giving nutrients to the cardiac muscles while removing toxic waste. In the quest to engineer transplantable organs, researchers must consider how to build comparable blood-vessel networks. © SPL/SCIENCE SOURCE
LIFELINES: The arteries and veins of the human heart (shown here injected with dyed gelatin) are critical to the organ’s function, with blood flow delivering life-giving nutrients to the cardiac muscles while removing toxic waste. In the quest to engineer transplantable organs, researchers must consider how to build comparable blood-vessel networks. © SPL/SCIENCE SOURCE
Thousands of unfortunate patients are badly in need of a replacement organ. As of April 2014, more than 122,000 such people in the United States were on the waiting list maintained by the national Organ Procurement and Transplant Network. But fewer than 30,000 of those patients will actually receive the transplant surgery they need this year. That’s because living or deceased donors constitute the only source of new organs, one that for years has not been able to keep pace with demand.
As the number of patients with severe, irreversible organ damage continues to rise, this gap will only widen. To fill the need, researchers are exploring whether they can build functional organs from scratch. Since the 1980s and 1990s, scientists and surgeons have used ...




















