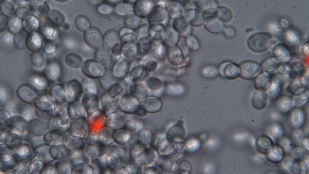
 A yeast cluster with dead cells shown in redWILLIAM RATCLIFF, UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA
A yeast cluster with dead cells shown in redWILLIAM RATCLIFF, UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA
In as little as 100 generations, yeast selected to settle more quickly through a test tube evolved into multicellular, snowflake-like clusters, according to a paper published today (January 16) in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Over the course of the experiment, the clusters evolved to be larger, produce multicellular progeny, and even show differentiation of the cells within the cluster—all key characteristics of multicellular organisms.
“It’s very cool to demonstrate that [multicellularity] can happen so quickly,” said evolutionary biologist Mansi Srivastava of the Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research in Massachusetts, who was not involved in the research. “Looking at the fossil record, we learned it took a very long time whenever these different transitions to multicellularity happened. Here they show it can happen ...












