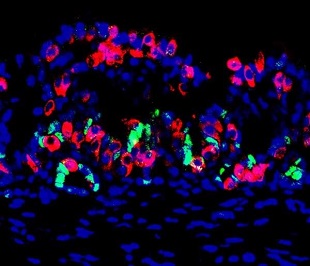
 A section of the mini stomach with cell nuclei (blue), insulin-producing cells (red), and gastric stem and progenitor cells (green)CHAIYABOOT ARIYACHET (VIA EUREKALERT)In type I diabetes, insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas are destroyed by the immune system, reducing an individual’s capacity to regulate glucose levels in the blood. Now a team led by researchers at Harvard has reported a new method to create personalized insulin-producing organs in vitro, which can restore normal blood-glucose levels when transplanted into mice with the disease. The findings were published last week (February 18) in Cell Stem Cell.
A section of the mini stomach with cell nuclei (blue), insulin-producing cells (red), and gastric stem and progenitor cells (green)CHAIYABOOT ARIYACHET (VIA EUREKALERT)In type I diabetes, insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas are destroyed by the immune system, reducing an individual’s capacity to regulate glucose levels in the blood. Now a team led by researchers at Harvard has reported a new method to create personalized insulin-producing organs in vitro, which can restore normal blood-glucose levels when transplanted into mice with the disease. The findings were published last week (February 18) in Cell Stem Cell.
“In various disease states, you have a constant loss of beta cells,” study coauthor Qiao Zhou of Harvard University said in a statement. “We provide, in principle, an advantage to replenish those.”
Cells in a region called the pylorus, between the stomach and the small intestine, frequently regenerate and also show several similarities in gene expression to beta cells. When the researchers engineered mice that expressed three genes known to promote beta cell production, they found that these pylorus cells were converted into insulin-secreting cells, and could restore normal glucose levels in the blood.
“We looked all over, from the nose to the tail of the mouse,” said Zhou in the statement. “We discovered, surprisingly, that some of the cells in the pylorus region of ...














