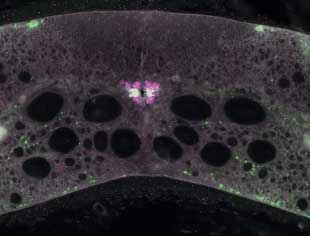
 NEUTRALIZERS: Cells in the lamprey spinal cord have PKD2L1 receptors (pink) that detect alkaline pH and produce somatostatin (green) to lower it. NOBEL INSTITUTE FOR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY, ELHAM JALALVAND
NEUTRALIZERS: Cells in the lamprey spinal cord have PKD2L1 receptors (pink) that detect alkaline pH and produce somatostatin (green) to lower it. NOBEL INSTITUTE FOR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY, ELHAM JALALVAND
The paper E. Jalalvand et al., “The spinal cord has an intrinsic system for the control of pH,” Curr Biol, 26:1346-51, 2016. pH swings Bodies like to keep their pH close to 7.4, whether that means hyperventilating to make the blood alkaline, or burning energy, shifting to anaerobic metabolism, and producing lactate to make the blood acidic. The lungs and kidneys can regulate pH changes systemically, but they may not act quickly on a local scale. Because even small pH changes can dramatically affect the nervous system, a study led by Sten Grillner of Karolinska Institute in Sweden looked for a mechanism for pH homeostasis in the spinal cord. Channeling change Using the lamprey as a model system, the researchers observed that a type of ...




















