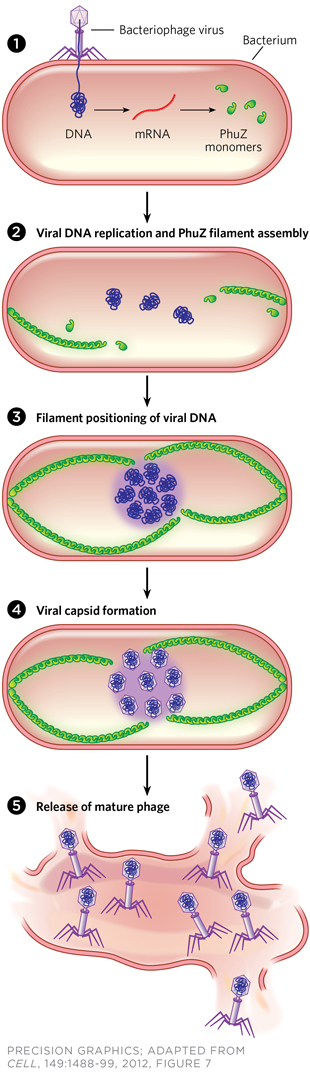
 PhuZed Phage: When phage infect bacteria, host proteins begin transcribing a viral gene to produce PhuZ proteins (1), which form tubulin-like polymers that elongate from each pole of the cell (2). The filaments position replicating viral DNA at the cell’s center (3). Newly made viral DNA is encased in capsids (4), and released by lysis from the cell after final assembly (5) to infect other bacteria.
PhuZed Phage: When phage infect bacteria, host proteins begin transcribing a viral gene to produce PhuZ proteins (1), which form tubulin-like polymers that elongate from each pole of the cell (2). The filaments position replicating viral DNA at the cell’s center (3). Newly made viral DNA is encased in capsids (4), and released by lysis from the cell after final assembly (5) to infect other bacteria.
THE PAPERJ.A. Kraemer et al., “A phage tubulin assembles dynamic filaments by an atypical mechanism to center viral DNA within the host cell,” Cell, 149:1488-99, 2012.Until a few years ago, the cytoskeleton was thought to be a structure unique to eukaryotes, but a stream of discoveries in the past decade has shown that prokaryotes also have actin- and tubulin-like components. Tubulins are proteins that form microtubules, which manage everything from sorting genetic material during cell division to supporting cell shape and assisting in cell motility. A collaboration between David Agard’s group at the University of California, San Francisco, and Joe Pogliano’s lab at UC San Diego has now shown that a bacteriophage virus also encodes a family of tubulin-like proteins, which appear to determine the ...














