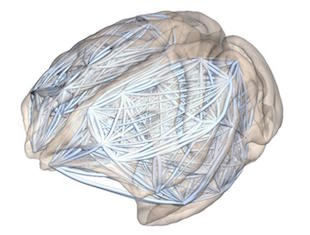
 Macaque brain networkSZABOLCA HORVÁTFrom those of mice to monkeys, the brain follows a consistent principle of organization. Scientists from the University of Notre Dame in South Bend, Indiana, and colleagues found that the brain follows an exponential distance rule whereby the strength of connections decreases with distance. Macaque brains have weaker long-distance connections than mouse brains do, which could explain why larger brains are more susceptible to disorders such as schizophrenia and Alzheimer’s disease, the researchers reported yesterday (July 21) in PLOS Biology.
Macaque brain networkSZABOLCA HORVÁTFrom those of mice to monkeys, the brain follows a consistent principle of organization. Scientists from the University of Notre Dame in South Bend, Indiana, and colleagues found that the brain follows an exponential distance rule whereby the strength of connections decreases with distance. Macaque brains have weaker long-distance connections than mouse brains do, which could explain why larger brains are more susceptible to disorders such as schizophrenia and Alzheimer’s disease, the researchers reported yesterday (July 21) in PLOS Biology.
“Using tract tracing data from macaque and mouse, we show the existence of a general organizational principle based on an exponential distance rule (EDR) and cortical geometry, enabling network comparisons within the same model framework,” the researchers wrote in their study.
Previously, Notre Dame’s Zoltán Toroczkai, along with Henry Kennedy of the University Lyon, France, and their colleagues, used a combination of tracing studies and network theory to show that primate brains follow the EDR, which predicts that there are many fewer long-range connections than short-range ones. In the present study, the team used similar methods to compare the organization of a macaque brain with the much smaller mouse brain. Both organs followed the same principle of connectivity, suggesting evolution has conserved this wiring principle.
...




















