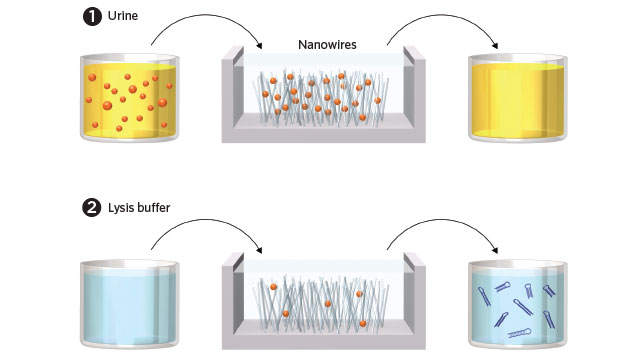
 PEE IN, MICRORNAs OUT: (1) A small volume of urine is introduced into the microfluidic device, where positively charged zinc oxide nanowires attract and bind negatively charged exosomes. (2) Lysis buffer is introduced to the device to break open the exosomes and free the microRNAs, which are then collected for sequence analysis.
PEE IN, MICRORNAs OUT: (1) A small volume of urine is introduced into the microfluidic device, where positively charged zinc oxide nanowires attract and bind negatively charged exosomes. (2) Lysis buffer is introduced to the device to break open the exosomes and free the microRNAs, which are then collected for sequence analysis.
See full infographic: WEB© GEORGE RETSECK
Exosomes are tiny membrane-bound packages that are released from practically every cell type and found in a wide range of body fluids. Containing RNAs, proteins, and other cell components, they are believed to be involved in communication between cells, and there’s evidence that their abundance and content may change with disease state. Consequently, there is a growing interest in collecting and analyzing these vesicles for diagnostic purposes. Researchers who are interested in the diagnostic potential of microRNAs, for example, are especially keen to collect exosomes because the RNAs they contain degrade more slowly than free-floating RNAs.
“They are packed with ...



















