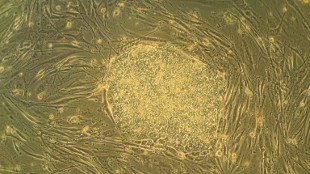
 A colony of embryonic stem cells surrounded by mouse fibroblastsWikimedia, Ryddragyn California-based BioTime Inc. announced yesterday (January 7) that it will buy Geron Corporation’s human embryonic stem cell (hESC) assets, which includes intellectual property, 400 patents and patent applications, and the first ever US Food and Drug Administration-approved Phase I clinical trial of a hESC therapy. The deal, which follows a letter of intent last October outlining just such a purchase and comes more than a year after Geron shutdown its hESC research, is backed by $10 million from a private investor and will leave Geron with roughly 6.5 million shares of BioTime subsidiary, BioTime Acquisition Corporation (BAC). Geron will also receive royalties on any sales of future products related to the hESC program.
A colony of embryonic stem cells surrounded by mouse fibroblastsWikimedia, Ryddragyn California-based BioTime Inc. announced yesterday (January 7) that it will buy Geron Corporation’s human embryonic stem cell (hESC) assets, which includes intellectual property, 400 patents and patent applications, and the first ever US Food and Drug Administration-approved Phase I clinical trial of a hESC therapy. The deal, which follows a letter of intent last October outlining just such a purchase and comes more than a year after Geron shutdown its hESC research, is backed by $10 million from a private investor and will leave Geron with roughly 6.5 million shares of BioTime subsidiary, BioTime Acquisition Corporation (BAC). Geron will also receive royalties on any sales of future products related to the hESC program.
“Our consistent goal at BioTime has been to consolidate the pluripotent stem cell technology platform,” Michael West, former chief executive officer (CEO) of Geron and current BioTime CEO, said in a statement. “With this contribution of assets, the combined intellectual property estate in the BioTime family of companies will be among the strongest in the field of regenerative medicine, establishing our leadership in the industry and advancing product development.”
Geron, based in Menlo Park, California, was a front-runner in the regenerative medicine field beginning in the 1990s, but abruptly ended its auspicious hESC research in 2011 for financial reasons and to focus on its telomerase-related cancer treatments. The move was seen as a significant misstep by many researchers and biotech companies in the field.
To ...


















