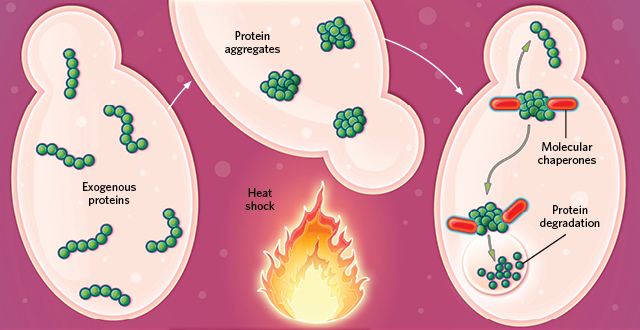
 SHOCKED OUT OF SHAPE: Exogenous proteins in a cell denature and aggregate in misfolded clumps when heat-shocked. During cell recovery, specialized molecular chaperone proteins degrade and dispose of the aggregates. A small portion of the exogenous proteins may refold, escaping degradation.© EVAN OTO/SCIENCE SOURCE
SHOCKED OUT OF SHAPE: Exogenous proteins in a cell denature and aggregate in misfolded clumps when heat-shocked. During cell recovery, specialized molecular chaperone proteins degrade and dispose of the aggregates. A small portion of the exogenous proteins may refold, escaping degradation.© EVAN OTO/SCIENCE SOURCE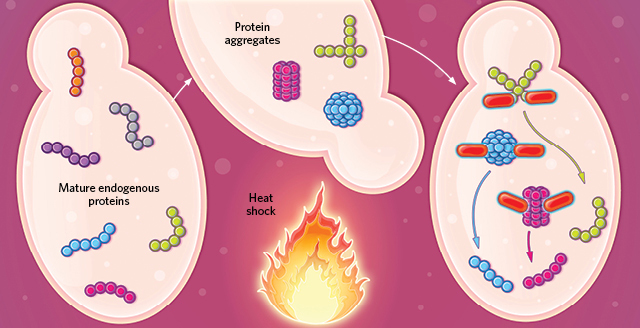 Mature endogenous proteins aggregate in an organized fashion when heat-shocked, remodeling the cell’s protein synthesis machinery to facilitate survival. During recovery, molecular chaperones free the mature proteins to resume their normal activity.© EVAN OTO/SCIENCE SOURCE
Mature endogenous proteins aggregate in an organized fashion when heat-shocked, remodeling the cell’s protein synthesis machinery to facilitate survival. During recovery, molecular chaperones free the mature proteins to resume their normal activity.© EVAN OTO/SCIENCE SOURCE
The paper
E.W.J. Wallace et al., “Reversible, specific, active aggregates of endogenous proteins assemble upon heat stress,” Cell, 162:1286-98, 2015.
Like cooking an egg, heating up a purified protein enough will denature it, destroying the 3-D structure key to its functionality. The protein unfolds in a one-way trip to a fried state. Previous studies of this phenomenon in cells often used exogenous proteins, which clumped together in response to heat and were largely degraded by the cell’s internal cleanup machinery—a set of molecular chaperones known as heat-shock proteins—if the cell survived.
“That, and other examples, had convinced people that what they were seeing inside cells, the clumps of proteins, represented a disaster—these giant piles of damaged proteins shoved together inside the cell so they can ...



















