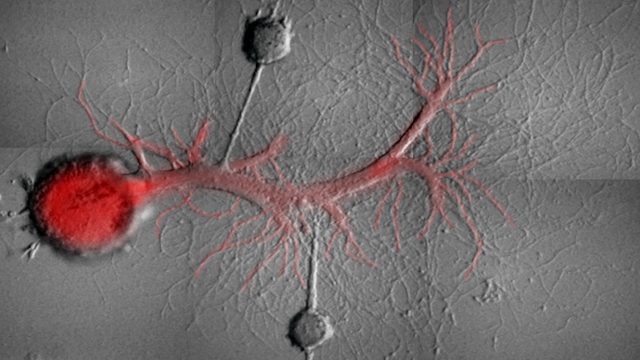
 Two Aplysia sensory neurons (dark grey) with synaptic contacts on a motor neuron (red)SCHACHER LAB/COLUMBIA UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTER
Two Aplysia sensory neurons (dark grey) with synaptic contacts on a motor neuron (red)SCHACHER LAB/COLUMBIA UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTER
By blocking specific enzymes, researchers were able to selectively remove memories stored in the neurons of Aplysia, a sea slug. These findings, published last week (June 22) in Current Biology, demonstrate that distinct memories stored in connections to a single nerve cell can be manipulated separately.
“We were able to reverse long-term changes in synaptic strength at synapses known to contribute to different forms of memories,” study coauthor Samuel Schacher, a neuroscientist at Columbia University, told Motherboard.
By stimulating multiple Aplysia sensory neurons that make connections with to the same motor neuron, Schacher and colleagues induced associative memory, which involves learning the relationship between two previously unrelated items (a new acquaintance’s name, for example), and non-associative memory, where recollections are unrelated to a specific event. ...




















