 STIMULATING VISION:
STIMULATING VISION:
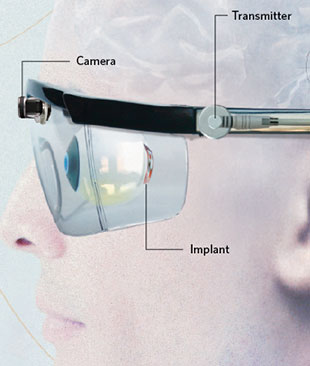
See full infographic: JPG | PDF© VIKTOR KOENIn 1755, French physician and scientist Charles Leroy discharged the static electricity from a Leyden jar—a precursor of modern-day capacitors—into a blind patient’s body using two wires, one tightened around the head just above the eyes and the other around the leg. The patient, who had been blind for three months as a result of a high fever, described the experience like a flame passing downwards in front of his eyes. This was the first time an electrical device—serving as a rudimentary prosthesis—successfully restored even a flicker of visual perception.
More than 250 years later, blindness is still one of the most debilitating sensory impairments, affecting close to 40 million people worldwide. Many of these patients can be efficiently treated with surgery or medication, but some pathologies cannot be corrected with existing treatments. In particular, when light-receiving photoreceptor cells degenerate, as is the case in retinitis pigmentosa, or when the optic nerve is damaged as a result of glaucoma or head trauma, no surgery or medicine can restore the lost vision. In such cases, a visual prosthesis may be the only option. Similar to cochlear implants, which stimulate auditory nerve fibers downstream of damaged sensory hair cells to restore hearing, visual prostheses aim to provide patients with visual information by stimulating neurons in the retina, ...




















