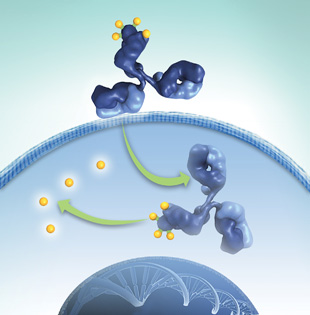
 CANCER SNIPERS: ImmunoGen’s Targeted Antibody Payload (TAP) technology features highly potent cytotoxic agents (yellow) attached to antibodies (blue) for targeted delivery to cancer cells.COURTESY OF IMMUNOGENThe early 1990s were not a good time to be in antibody research. Once hailed as “magic bullets,” antibodies repeatedly failed in clinical trials for cancer treatments during the ’80s, and money and interest in the sector dried up. So when researchers at ImmunoGen, a small biotech in Waltham, Massachusetts, had the idea to use antibodies as vehicles to shuttle toxins to a tumor, they were largely ignored. “We wanted to present posters at meetings, but if we had ‘antibody’ in the title, no one would look at it,” says John Lambert, ImmunoGen’s chief scientific officer.
CANCER SNIPERS: ImmunoGen’s Targeted Antibody Payload (TAP) technology features highly potent cytotoxic agents (yellow) attached to antibodies (blue) for targeted delivery to cancer cells.COURTESY OF IMMUNOGENThe early 1990s were not a good time to be in antibody research. Once hailed as “magic bullets,” antibodies repeatedly failed in clinical trials for cancer treatments during the ’80s, and money and interest in the sector dried up. So when researchers at ImmunoGen, a small biotech in Waltham, Massachusetts, had the idea to use antibodies as vehicles to shuttle toxins to a tumor, they were largely ignored. “We wanted to present posters at meetings, but if we had ‘antibody’ in the title, no one would look at it,” says John Lambert, ImmunoGen’s chief scientific officer.
Around the same time, a company with a similar idea opened its doors on the West Coast. Molecular biologist Clay Siegall was enthusiastic about the idea of “empowered antibodies”—antibodies armed with a chemical “warhead” to blast tumor cells to oblivion—but his employer, pharmaceutical company Bristol-Myers Squibb, was not. In fact, the company shut down its targeted antibody program in 1997. So Siegall left and founded Seattle Genetics to pursue the idea.
Both companies, it turns out, were onto something good. They were developing what are now known as antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs)—today an established and active area of pharmaceutical research. In August 2011, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the first in a new class of ADCs—Seattle Genetics’ Adcetris—after only phase II trials because ...
















