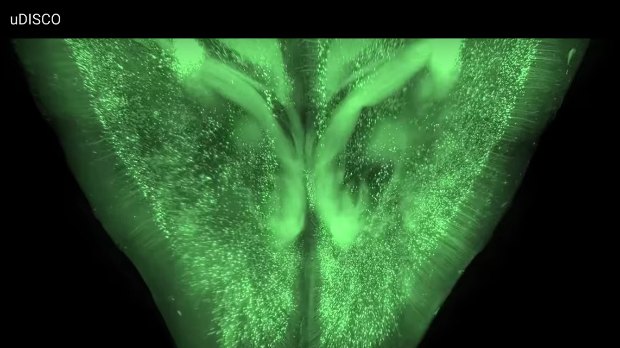
 YOUTUBE, ALI ERTURKA variety of techniques sweep away lipids and other opaque molecules to create see-through biological samples, including whole animals. Reporting in Nature Methods yesterday (August 22), scientists presented a tissue-clearing protocol that shrinks tissue to expand the limits of how big samples can be for imaging.
YOUTUBE, ALI ERTURKA variety of techniques sweep away lipids and other opaque molecules to create see-through biological samples, including whole animals. Reporting in Nature Methods yesterday (August 22), scientists presented a tissue-clearing protocol that shrinks tissue to expand the limits of how big samples can be for imaging.
“We imaged the complete central nervous system of mice, and you can track individual cells several centimetres long that reach from the brain right through to the tip of the spinal cord,” study coauthor Ali Ertürk of the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich in Germany told New Scientist.
Ertürk and colleagues built upon a procedure called 3-D imaging of solvent-cleared organs (DISCO). Although DISCO shrinks samples, it “quickly quenches endogenously expressed fluorescent proteins (with a half-life of a few days),” the authors point out in their report. They searched for solvents that could clear tissue without destroying fluorescence and settled upon diphenyl ether. Their recipe, called “ultimate DISCO,” maintains fluorescence for months.
“I love it,” Ingo Bechmann, a neuroscientist at the University of Leipzig, Germany, ...





















