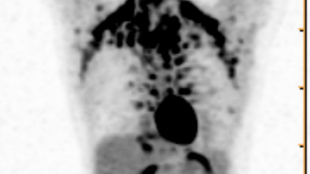
 WIKIMEDIA, HELLERHOFFThe stimulation of so-called brown fat—the energy-burning kind—is thought to be a potential therapeutic target for obesity. In a study published in Cell Metabolism this month (January 6), researchers gave volunteers an already-approved drug, which, as it turned out, appeared to stimulate metabolism and the activity of brown fat.
WIKIMEDIA, HELLERHOFFThe stimulation of so-called brown fat—the energy-burning kind—is thought to be a potential therapeutic target for obesity. In a study published in Cell Metabolism this month (January 6), researchers gave volunteers an already-approved drug, which, as it turned out, appeared to stimulate metabolism and the activity of brown fat.
The drug, mirabegron, acts as an agonist of β3-adrenergic receptors and is given to patients who experience overactive bladder. “Brown adipose tissue, or brown fat, produces β3-adrenergic receptor at levels higher than nearly every other organ in the body. We showed that a one-time dose of the drug mirabegron stimulates human brown adipose tissue so that it consumes glucose and burns calories,” study coauthor Aaron Cypess of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases said in a statement.
The researchers estimated that at the 200 milligram dose used in the study, men taking mirabegron could lose around five kilograms (11 pounds) in the first year, and 10 kilograms (22 pounds) after three years of treatment. “Though promising, the actual amount of weight ...



















