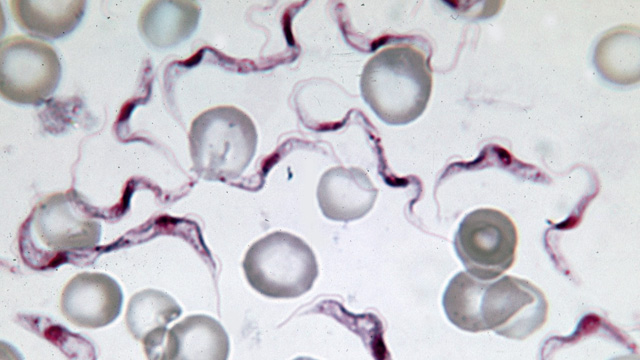
 TRYPANOSOMA BRUCEI PROTOZOA: The parasite, shown here in purple, causes sleeping sickness, a disease that starts out as fever and inflammation and progresses to neurological symptoms such as confusion and disrupted sleep cycles, eventually leading to coma and death. WIKIMEDIA COMMONS, ALAN R. WALKER
TRYPANOSOMA BRUCEI PROTOZOA: The parasite, shown here in purple, causes sleeping sickness, a disease that starts out as fever and inflammation and progresses to neurological symptoms such as confusion and disrupted sleep cycles, eventually leading to coma and death. WIKIMEDIA COMMONS, ALAN R. WALKER
S. Alsford et al., “High-throughput decoding of antitrypanosomal drug efficacy and resistance,” Nature, 482:232-36, 2012.
Trypanosoma brucei, the single-cell protozoan that causes the tropical disease sleeping sickness, is becoming increasingly resistant to the few drug treatments available. Using RNA interference (RNAi), David Horn of the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine and colleagues identified 55 genes that contribute to drug susceptibility and resistance.
Horn used a library of plasmids to create around 750,000 T. brucei clones, each with one of the bug’s 7,500 or so genes knocked down using RNAi. He then treated the pool with five different sleeping sickness drugs, selecting for those clones that gained resistance by losing a gene. Using next-generation sequencing, the team identified 55 susceptibility-related genes in the survivors, ...




















