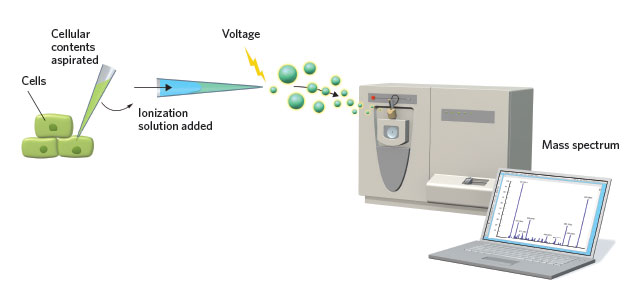
 SINGLE-CELL MASS SPEC: To analyze the small-molecule components of an individual cell, a tiny capillary needle sucks material from the cytoplasm. After mixing the contents with an ionization solution, an applied voltage ejects the material from the needle and sends it into a mass spectrometer for analysis.
SINGLE-CELL MASS SPEC: To analyze the small-molecule components of an individual cell, a tiny capillary needle sucks material from the cytoplasm. After mixing the contents with an ionization solution, an applied voltage ejects the material from the needle and sends it into a mass spectrometer for analysis.
See full infographic: PDF© GEORGE RETSECK
Analyzing the molecular constituents of a homogenized piece of animal or plant tissue may provide clues about the nature of the component cells’ functions. But it may also obscure striking functional differences between individual cells.
Not surprisingly, then, the study of single cells is a burgeoning area of research. While single-cell genomics and transcriptomics have benefited from DNA’s and RNA’s inherent ability to be amplified, single-cell proteomics and metabolomics must rely solely on miniscule quantities of starting material.
Researchers have thus been developing a variety of techniques for tackling such tiny volumes. The teams of Tsutomu Masujima at Hiroshima University and RIKEN in Osaka, Japan, for example, have been perfecting a mass spectrometry protocol for examining plant-cell metabolites that requires micromanipulation tools similar to those ...
















