The therapeutic potential of targeting glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) has become increasingly evident over the past 20 years, both as notable diabetes and weight loss drugs, such as exenatide, liraglutide, and semiglutide, and as drug candidates beyond insulin regulation. Research in this field has progressed from a niche focus on diabetes to a powerful therapeutic platform with far-reaching implications for human health.
Looking beyond GLP-1 as a singular drug target and considering its multifaceted roles in metabolism may help scientists uncover treatment opportunities in cardiovascular and neurological diseases. In this Innovation Spotlight, Dale Wright, executive director of inflammation & systems biology and Brian Bond, vice president of drug discovery and translational sciences at Inotiv, discuss the importance of taking a holistic approach to GLP-1 therapeutic research using systems pharmacology.

Dale Wright
Executive Director
Inflammation & Systems Biology
Inotiv
Where did the GLP-1 research field begin and how is it evolving?
Brian Bond: Initial research discoveries in the 1980s and 1990s highlighted GLP-1’s role in glucose metabolism and appetite regulation, paving the way for the first GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) used for type 2 diabetes treatment.1 Since then, the field has evolved dramatically. The success of early GLP-1 therapies, such as exenatide and liraglutide, inspired further research into their broader metabolic and cardiovascular benefits.
Dale Wright: Today, GLP-1-based drugs are revolutionizing not only diabetes management but also obesity treatment, and show promise in addressing conditions such as metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), cardiovascular disease, and neurodegenerative disorders. Advances in drug design, such as dual and triple agonists (e.g., GLP-1/gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP) and GLP-1/GIP/glucagon receptor agonists), are expanding the therapeutic impact of these molecules, making GLP-1 one of the most exciting areas in drug development.

Brian Bond, PhD
Vice President
Drug Discovery & Translational Sciences Inotiv
What makes GLP-1 RAs particularly enticing for scientists doing drug discovery research?
Bond: GLP-1 RAs offer a unique combination of metabolic benefits, which makes them highly attractive for drug discovery. Unlike traditional insulin therapies, GLP-1 RAs enhance insulin secretion only when blood glucose levels are elevated, reducing the risk of hypoglycemia. By acting on the central nervous system, GLP-1 RAs decrease appetite and promote weight loss, making them valuable in obesity treatment. Additionally, emerging evidence shows that GLP-1 therapies lower cardiovascular risk, reduce inflammation, and improve lipid metabolism, independent of glucose control and weight loss, opening doors to broader applications. Preclinical and clinical studies also suggest that GLP-1 RAs may slow cognitive decline and provide therapeutic benefits in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. These multi-faceted effects are driving intense research efforts to develop more potent and longer-lasting GLP-1-based therapies as well as the discovery of mechanism related new targets.
What are systems biology and systems pharmacology? How do these approaches uniquely support therapeutic research?
Wright: A systems biology or a systems pharmacology approach is a data-driven approach that integrates multi-omics and network biology to understand disease mechanisms at a holistic level. Applying these insights can help one understand how drugs interact with biological networks and optimize drug target interactions and safety. These advanced methodologies expedite drug development, bridging the gap between preclinical research and clinical success. Inotiv is committed to partnering with researchers to unlock deeper drug discovery insights through this approach.
Bond: Inotiv’s drug discovery engine strategically runs with the critical components that are required to provide insights into the mechanism of therapeutic intervention, the safety of novel therapies, and the predicted clinical success of drug discovery programs. By integrating expertise from early drug discovery through investigational new drug (IND) filing and beyond, Inotiv streamlines the path from discovery to clinical success.
What are the disease areas that Inotiv is interested in as the next frontier for GLP-1 therapeutic research?
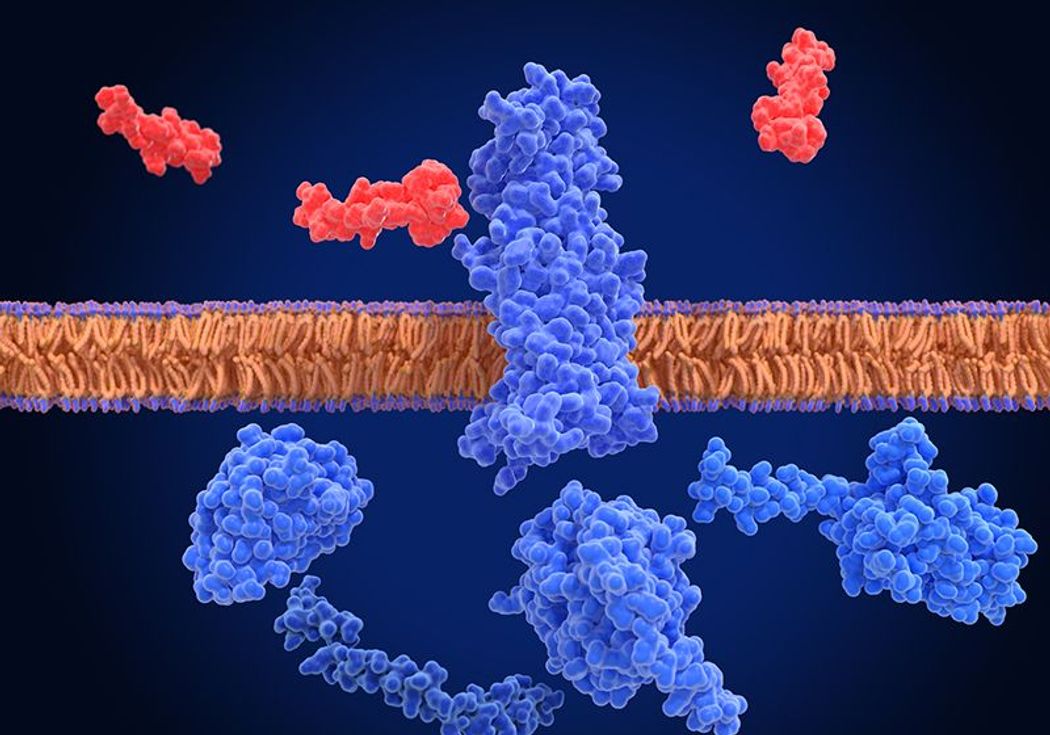
GLP-1 RAs activate the GLP-1 receptor in a glucose-dependent manner to enhance insulin secretion, posing a lower risk of hypoglycemia than traditional insulin therapies.
iStock, selvanegra
Wright: One of many benefits that Inotiv brings is that the drug discovery engine is strategically built to support many different therapeutic and disease areas. While diabetes and obesity remain the core areas of GLP-1 drug development, GLP-1 has been shown to affect multiple pathways branching into therapeutic and disease areas such as cardiovascular, neurodegenerative, and gastrointestinal disease. Inotiv’s sophisticated bioanalytical and system pharmacology platforms, coupled with in vitro and in vivo models across many disease areas, help bridge the gap between preclinical findings and human applications. This approach aims to de-risk drug development across numerous therapeutic programs.
What excites you the most about the future of GLP-1 drug discovery research?
Wright: GLP-1 therapeutics seem to offer promise in several disease areas. That is the exciting part; as we see many benefits within other diseases outside of diabetes and obesity. Understanding their impact on these conditions and recognizing the potential to influence other diseases, fuels scientific research and the excitement GLP-1 RAs may have in improving the lives of many.
What also excites researchers is the convergence of pharmacology, AI-driven drug discovery, and personalized medicine. The potential for once-weekly or even oral GLP-1 formulations, novel receptor co-agonists, and precision medicine approaches could transform treatment paradigms across multiple diseases.
- Zhao X, et al. GLP-1 receptor agonists: Beyond their pancreatic effects. Front Endocrinol. 2021;12:721135.














