 ENIKO KUBINYIDogs and humans process sounds similarly, according to a comparative neuroimaging study published in Current Biology this week (February 20). Using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) on dogs and humans listening to experimental sounds and silent controls, researchers from Eötvös Loránd University in Budapest and the Hungarian Academy of Sciences found that both species responded most strongly to conspecific vocalizations and processed vocal cues in similar parts of the brain.
ENIKO KUBINYIDogs and humans process sounds similarly, according to a comparative neuroimaging study published in Current Biology this week (February 20). Using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) on dogs and humans listening to experimental sounds and silent controls, researchers from Eötvös Loránd University in Budapest and the Hungarian Academy of Sciences found that both species responded most strongly to conspecific vocalizations and processed vocal cues in similar parts of the brain.
Gregory Berns of Emory University in Atlanta, Georgia, who was not involved in the work, told The Scientist that whereas most comparative fMRI work has focused on humans and nonhuman primates, this study “is really interesting because it’s looking at comparative anatomy and auditory processing between dogs and humans.”
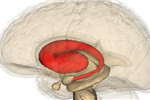 WIKIMEDIA, LIFE SCIENCE DATABASESome neurons in the human striatum are renewed through adult life, researchers have found. Jonas Frisén from the Karolinska Institute in Sweden and his colleagues used a variety of techniques—including 14C dating—to show that interneurons in the striatum were regularly replaced. They published their results in Cell this week (February 20).
WIKIMEDIA, LIFE SCIENCE DATABASESome neurons in the human striatum are renewed through adult life, researchers have found. Jonas Frisén from the Karolinska Institute in Sweden and his colleagues used a variety of techniques—including 14C dating—to show that interneurons in the striatum were regularly replaced. They published their results in Cell this week (February 20).
“This is the clearest demonstration that [adult neurogenesis in the striatum] is happening in humans,” said Arnold Kriegstein, a University of California, San Francisco, developmental neurobiologist who was not involved in the study. “It reenergizes the notion that . . . in the future, it would be possible to harness these ...




















