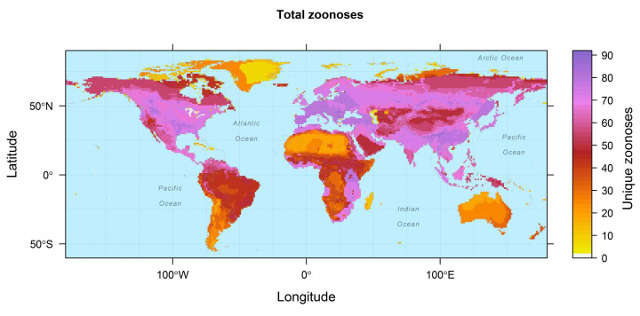
 Overlapping geographic ranges of zoonotic diseases carried by wild terrestrial mammal host species from 27 ordersDREW KRAMERCompiling data from hundreds of studies on past zoonotic disease outbreaks, Barbara Han, a disease ecologist at the Cary Institute of Ecosystem Studies in Millbrook, New York, and her colleagues have mapped where current reservoirs are most likely to be found. The goal was to be able to predict where future pathogenic leaps from mammals to humans are likely to occur.
Overlapping geographic ranges of zoonotic diseases carried by wild terrestrial mammal host species from 27 ordersDREW KRAMERCompiling data from hundreds of studies on past zoonotic disease outbreaks, Barbara Han, a disease ecologist at the Cary Institute of Ecosystem Studies in Millbrook, New York, and her colleagues have mapped where current reservoirs are most likely to be found. The goal was to be able to predict where future pathogenic leaps from mammals to humans are likely to occur.
“What we really want to do is shift the strategy from one of being defensive—always running around putting out fires—to one that’s preemptive,” Han told The Washington Post. “One step toward that goal is to figure out where things are, what’s carrying the known diseases and what’s their distribution.”
But the results, published today (June 14) in Trends in Parasitology, are only a piece of the puzzle, she added. “It’s a hard game to play because there’s hundreds and hundreds of combinations of different zoonoses and carriers. We’d hoped to find a unifying theme, and instead there’s just 45 more questions that need to be answered.”
Zoonotic diseases are not, for example, concentrated in tropical environments, as might be predicted. In fact, the subarctic—Alaska, northern ...


















