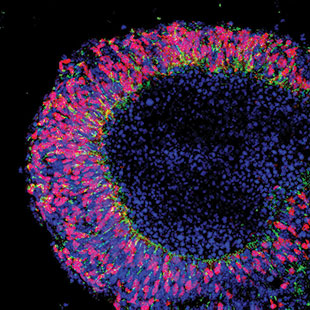
 REGROWING RETINAS: By culturing mouse embryonic stem cells, researchers can grow nascent retinas containing photoreceptor precursors that express the visual pigment rhodopsin (green) and the transcription factor Crx (red) and can be isolated and transplanted into adult mice.IMAGE BY ANAI GONZALEZ-CORDERIn mid-June, Newark, California–based StemCells, Inc. announced interim results of its ongoing Phase 1/2 trial for the treatment of dry age-related macular degeneration, a form of progressive blindness common in the elderly. Seven patients with advanced disease who had been dosed with the experimental therapeutic—multipotent neural stem cells derived from fetal brain tissue—showed slowed retinal atrophy at one year post-transplant, and four had not just stabilized but improved visual function, the company reported.
REGROWING RETINAS: By culturing mouse embryonic stem cells, researchers can grow nascent retinas containing photoreceptor precursors that express the visual pigment rhodopsin (green) and the transcription factor Crx (red) and can be isolated and transplanted into adult mice.IMAGE BY ANAI GONZALEZ-CORDERIn mid-June, Newark, California–based StemCells, Inc. announced interim results of its ongoing Phase 1/2 trial for the treatment of dry age-related macular degeneration, a form of progressive blindness common in the elderly. Seven patients with advanced disease who had been dosed with the experimental therapeutic—multipotent neural stem cells derived from fetal brain tissue—showed slowed retinal atrophy at one year post-transplant, and four had not just stabilized but improved visual function, the company reported.
“They’ve actually had gains in their visual ability to sense contrast, which is the difference between light and dark,” explains Stephen Huhn, the company’s chief medical officer and vice president for central nervous system (CNS) clinical research. “It’s very powerful to see that this early in the trial.”
StemCells’ announcement is the latest in a series of promising developments in the area of cell-based therapeutics for blindness. Advanced Cell Technology (ACT) has several ongoing trials based on differentiated cells derived from human embryonic stem cells (hESCs), and last year, Japanese researchers launched the first clinical study to use induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) derived from adult human cells for the treatment of age-related macular degeneration. Still other strategies are in development, and excitement is high.
...


















