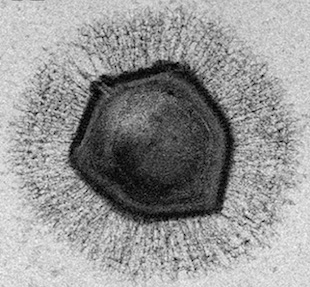
 Mimivirus particlePLOS PATHOGENS, E. GHIGO ET ALThe CRISPR/Cas defense system found in many bacteria, with its simple yet elegant method for editing a host genome, has become the biological technique of the moment, spurring a flood of recent discoveries. In March, Didier Raoult of the Aix-Marseille University in France and colleagues published a paper suggesting that a type of giant virus known as mimivirus possesses a virophage resistance mechanism—called mimivirus virophage resistance element, or MIMIVIRE—that resembles the CRISPR system. (See “Giant Virus Has CRISPR-like Immune Defense,” The Scientist, March 2, 2016.) In a perspective published last month (June 13) in Virologica Sinica, Jean-Michel Claverie and Chantal Abergel of France’s CNRS challenge this view.
Mimivirus particlePLOS PATHOGENS, E. GHIGO ET ALThe CRISPR/Cas defense system found in many bacteria, with its simple yet elegant method for editing a host genome, has become the biological technique of the moment, spurring a flood of recent discoveries. In March, Didier Raoult of the Aix-Marseille University in France and colleagues published a paper suggesting that a type of giant virus known as mimivirus possesses a virophage resistance mechanism—called mimivirus virophage resistance element, or MIMIVIRE—that resembles the CRISPR system. (See “Giant Virus Has CRISPR-like Immune Defense,” The Scientist, March 2, 2016.) In a perspective published last month (June 13) in Virologica Sinica, Jean-Michel Claverie and Chantal Abergel of France’s CNRS challenge this view.
“MIMIVIRE is not analogous to the CRISPR-Cas system, does not function via a nucleic acid recognition system, and is unlikely to possess all the attributes of a bona fide adaptive immune system,” Claverie and Abergel wrote in their paper. (Claverie and Raoult have worked together in the past; both told The Scientist they now have a contentious relationship.)
Claverie and Abergel go on to question whether the mimivirus virophage resistance mechanism is based on nucleic acids at all. They instead propose that proteins may be interfering with replication of virophage in the resistant mimivirus.
Giant viruses are named for their large size and massive genomes. They inhabit amoebas, and can themselves be infected by virophages. Raoult and colleagues discovered the Mimiviridae genus of mimiviruses in ...