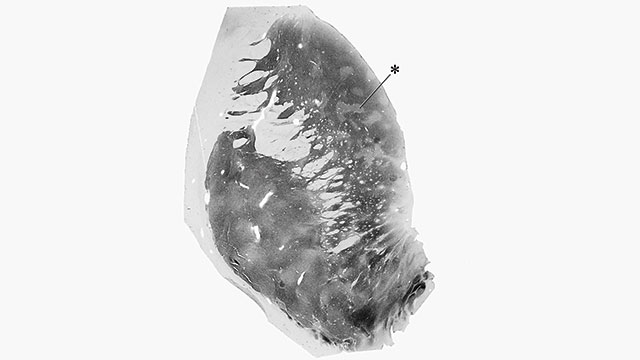
 TRICKY SPOT: Neural structures called striosomes, such as the one highlighted by an asterisk in this section of striatum from a human brain, may aid in complex decision making.GRAYBIEL LAB, MIT
TRICKY SPOT: Neural structures called striosomes, such as the one highlighted by an asterisk in this section of striatum from a human brain, may aid in complex decision making.GRAYBIEL LAB, MIT
Many of life’s trickier decisions share a common denominator: the options all have both pros and cons. This is what psychologists call a “cost-benefit conflict,” and it’s something that rats and mice in Ann Graybiel’s neuroscience laboratory at MIT face on a regular basis.
Graybiel aims to understand how brains evaluate costs and benefits, and why the capacity to do so is sometimes impaired in neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders such as Huntington’s disease, anxiety, and depression. Graybiel and her colleagues have pinpointed the specific brain circuit—consisting of prefrontal cortical neurons, neurons in structures known as striosomes, and inhibitory interneurons that suppress the activity of striosomes—that appears to control this type of decision making. In a study published last November, the researchers reported that chronic stress ...




















