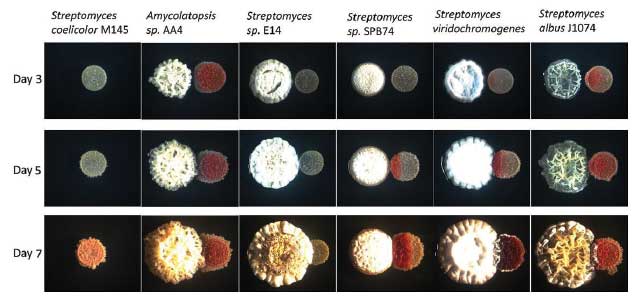
 MIXING IT UP: The bacterium Streptomyces coelicolor produces a variety of novel compounds when grown in combination with other bacterial species, and these interspecies interactions result in differences in colony development and pigment production when viewed under a microscope.mBio, doi:10.1128/mBio.00459-13, 2013
MIXING IT UP: The bacterium Streptomyces coelicolor produces a variety of novel compounds when grown in combination with other bacterial species, and these interspecies interactions result in differences in colony development and pigment production when viewed under a microscope.mBio, doi:10.1128/mBio.00459-13, 2013
Antibiotic resistance is a major threat to global health, and researchers have struggled to identify new antimicrobial compounds. By the late 1990s, the bacterial reservoirs from which almost all clinically useful antibiotics had sprung appeared to run dry. As bacterial genome sequencing became more widespread in the last decade, however, researchers discovered many potential sources of new drugs hidden in these genomes. Now they just need to learn how to mine them.
Most antibiotics are derived from small molecules produced by bacteria, and the genes that synthesize, regulate, and export these molecules typically occur together in groups called biosynthetic gene clusters, which range in size from just a handful to several dozen genes. Sequencing efforts have revealed that the genomes of antibiotic-producing organisms, such as ...























