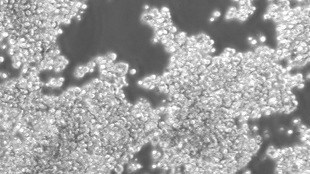
 F-class cellsLUNENFELD-TANENBAUM RESEARCH INSTITUTE/PETER D. TONGEResearchers from Mount Sinai Hospital’s Lunenfeld-Tanenbaum Research Institute and their international colleagues have uncovered a new type of pluripotent mouse stem cell—the “F-class” cell—through use of a somatic cell reprogramming approach. An F-class cell is able to differentiate into all three embryonic precursor tissues, yet is phenotypically and molecularly different from previously characterized induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) made from somatic cells. These F-class cells proliferate more quickly than other stem cells in vitro, and are characteristically low-adhesion, giving them a fuzzy appearance. The results are published today (December 10) in Nature.
F-class cellsLUNENFELD-TANENBAUM RESEARCH INSTITUTE/PETER D. TONGEResearchers from Mount Sinai Hospital’s Lunenfeld-Tanenbaum Research Institute and their international colleagues have uncovered a new type of pluripotent mouse stem cell—the “F-class” cell—through use of a somatic cell reprogramming approach. An F-class cell is able to differentiate into all three embryonic precursor tissues, yet is phenotypically and molecularly different from previously characterized induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) made from somatic cells. These F-class cells proliferate more quickly than other stem cells in vitro, and are characteristically low-adhesion, giving them a fuzzy appearance. The results are published today (December 10) in Nature.
“What I find particularly exciting is that this opens up the idea that there may be different kinds of pluripotent stem cells,” said Paul Knoepfler, a stem cell biologist at the University of California, Davis, who was not involved in the work.
Juan Carlos Izpisua Belmonte, a developmental biologist at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies in La Jolla, California, who penned an accompanying editorial, agreed. “These studies and our understanding of embryo development teach us that we shouldn’t assume the known pluripotent stem cells represent the whole spectrum of pluripotency. Rather, there exists a multitude of pluripotent states or novel pluripotent states can be engineered through cellular reprograming,” Belmonte told The Scientist in an e-mail.
A second Nature paper published today provides a detailed ...


















