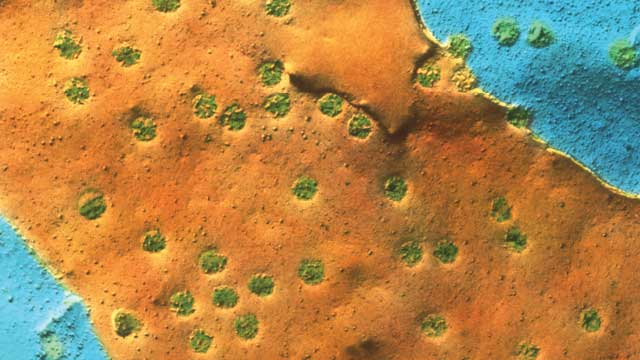
 DOTTED WITH PORES: This colored freeze-fracture transmission electron micrograph shows part of the nuclear envelope of a mouse liver cell. Nuclear pore complexes (green) penetrate both the inner (blue) and outer (brown) membranes, regulating transport into and out of the nucleus. © DR. KARI LOUNATMAA/SCIENCE SOURCE
DOTTED WITH PORES: This colored freeze-fracture transmission electron micrograph shows part of the nuclear envelope of a mouse liver cell. Nuclear pore complexes (green) penetrate both the inner (blue) and outer (brown) membranes, regulating transport into and out of the nucleus. © DR. KARI LOUNATMAA/SCIENCE SOURCE
Eukaryotic cells store their DNA in the nucleus, cordoned off from the cytoplasm by the nuclear envelope. Made up of two lipid bilayers called the inner and outer nuclear membrane, the nuclear envelope protects DNA from damage by reactive by-products and intermediates of cellular metabolism. It also serves as a critical regulator of gene expression, restricting access to the genome and dictating which transcripts can exit the nucleus. This regulatory responsibility ultimately belongs to the thousands of massive molecular machines that penetrate both nuclear membranes to form gateways between the nucleus and cytoplasm.
Each nuclear pore complex (NPC) consists of more than 1,000 individual protein subunits with a total molecular mass of approximately 120 million daltons—the equivalent of more than 6.5 million water molecules. The ...




















